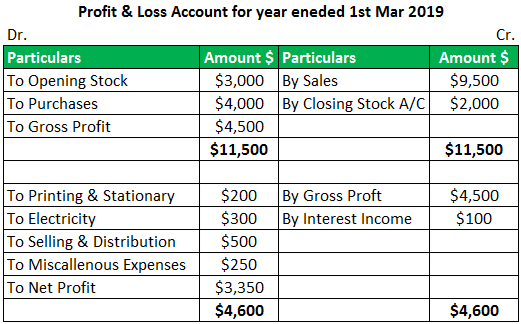
A Profit and Loss (P&L) account, also known as an income statement, is a financial statement that summarizes the revenues and expenses of a company over a specified period of time, typically a fiscal quarter or year. It provides information on the company's profitability by showing the difference between its total revenue and total expenses. The P&L statement is used by investors, lenders, and management to evaluate a company's financial performance and make informed decisions.A Profit and Loss (P&L) account, also known as an income statement, provides a summary of a company's revenues and expenses over a specified period of time, usually a fiscal quarter or year. The purpose of a P&L account is to give an idea of a company's financial performance by calculating its net income or net loss, which is obtained by subtracting total expenses from total revenues.
The P&L account typically includes the following information:
• Revenue: The total amount of money earned by the company through the sale of goods or services.
• Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): The direct costs associated with producing and selling the goods or services.
• Gross Profit: The difference between revenue and COGS, representing the amount of money made before deducting overhead expenses.
• Operating Expenses: Includes all other expenses incurred by the company, such as salaries, rent, marketing, and utilities.
• Operating Income: The amount of money left after subtracting operating expenses from gross profit.
• Other Income/Expense: Any other income or expense that does not fall into the categories listed above, such as interest income or loss on sale of assets.
• Net Income: The final result of the P&L account, calculated as the difference between total revenue and total expenses.
The P&L account is a crucial tool for investors, lenders, and management to evaluate the financial health and performance of a company. It provides insight into a company's revenue generation capabilities, cost structures, and overall profitability.
IMPORTANCE
The Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, also known as an income statement, is a key financial statement that provides important information on the financial performance of a company. The importance of a P&L statement can be summarized as follows:
1. Assesses Financial Performance: The P&L statement provides a comprehensive picture of a company's revenue and expenses over a given period, enabling the company to measure its financial performance and determine whether it is generating profits or losses.
2. Evaluates Business Efficiency: The P&L statement helps to assess the efficiency of a company's operations by showing the relationship between revenue and expenses, providing insights into areas where the company can reduce costs and increase profitability.
3. Facilitates Decision Making: By providing a clear picture of the financial performance of a company, the P&L statement helps management make informed decisions about the direction of the business, such as whether to invest in new products or services, or expand operations.
4.Helps Attract Investors and Lenders: The P&L statement is an important document for attracting investors and lenders, as it provides a clear and concise picture of the financial performance and stability of a company.
5.Supports Budgeting and Forecasting: The P&L statement is also used to create budgets and make financial projections, allowing companies to plan for future growth and stability.
In conclusion, the P&L statement is a critical tool for evaluating the financial health and performance of a company and making informed decisions about its future.
TYPES OF PROFIT AND LOSS
There are several types of Profit and Loss (P&L) accounts, including:
1. Single-Step P&L Statement: This type of P&L statement provides a simple calculation of net income by subtracting total expenses from total revenue.
2. Multi-Step P&L Statement: A multi-step P&L statement provides a more detailed breakdown of the components of net income. It includes gross profit, operating income, and net income, calculated through several intermediate steps.
3. Service Company P&L Statement: This type of P&L statement is specifically designed for service companies, which do not have inventory or cost of goods sold to consider. It provides a detailed breakdown of operating expenses and net income.
4. Manufacturing Company P&L Statement: This type of P&L statement is designed for companies that manufacture products, including both direct and indirect costs related to production.
5. Retail Company P&L Statement: This type of P&L statement is designed for retail companies, including costs such as merchandise purchases, freight and handling, and selling expenses.
6. Project P&L Statement: This type of P&L statement is used for individual projects or contracts, and provides a detailed breakdown of revenue and expenses specific to that project.
In conclusion, the type of P&L statement used depends on the nature of a company's operations and the level of detail required to evaluate its financial performance.
ADVANTAGES
Advantages of Profit and Loss (P&L) statements:
1.Provides insight into financial performance: P&L statements provide a comprehensive view of a company's financial performance over a given period of time, including its revenue, expenses, and net income.
2. Helps in decision making: P&L statements provide valuable information that can be used to make informed business decisions, such as whether to expand operations, invest in new products or services, or adjust pricing strategies.
3. Facilitates budgeting and forecasting: P&L statements can be used to create budgets and financial forecasts, which help companies plan for future growth and ensure that resources are allocated efficiently.
4. Facilitates monitoring of performance: P&L statements allow companies to monitor their performance over time, identify trends, and make necessary adjustments to improve financial performance.
DISADVANTAGES
1.Limited scope: P&L statements only provide a snapshot of financial performance for a given period of time, and do not provide a complete picture of a company's financial health.
2. Can be subject to manipulation: P&L statements are based on financial data that can be manipulated by companies to present a more favorable picture of their financial performance.
3. Does not account for non-financial factors: P&L statements do not account for non-financial factors, such as customer satisfaction or employee morale, which can have a significant impact on a company's long-term success.
4. Can be complex: P&L statements can be complex and difficult to understand for people without a background in finance, which can make it challenging for non-financial stakeholders to make informed decisions based on the information presented.
In conclusion, P&L statements provide valuable information about a company's financial performance, but they also have some limitations. It's important to use P&L statements in conjunction with other financial metrics and consider non-financial factors when evaluating a company's financial health and stability.
PROFIT AND LOSS FORMULA
The formula for calculating the net income on a Profit and Loss (P&L) statement is:
Net Income = Revenue - Expenses
Revenue is the total amount of money a company earns from its operations. Expenses include all the costs incurred by the company in order to generate revenue, including cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, and other income/expense.
The formula can be broken down further to calculate the gross profit, which is the amount of money a company earns from its operations before subtracting operating expenses:
Gross Profit = Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
And operating income, which is the amount of money a company earns from its operations after subtracting operating expenses:
Operating Income = Gross Profit - Operating Expenses
In conclusion, the formula for calculating net income on a P&L statement is a simple and straightforward calculation that provides a snapshot of a company's financial performance and is used to evaluate its efficiency and profitability. Understanding the formula is essential for companies and investors alike, as it provides a key metric for determining the overall financial health and stability of a business.
PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT FORMAT
The format of a Profit and Loss (P&L) statement is typically as follows:
1. REVENUE
The first section of the P&L statement lists the total amount of money earned by the company from its operations. This can include sales, fees, and other forms of revenue. Revenue is the top line item on a Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, also known as an income statement. It represents the total amount of money a company has earned through the sale of its goods or services during a specified period of time, typically a fiscal quarter or year.Revenue is a critical metric in determining a company's financial performance, as it provides insight into its ability to generate income. An increase in revenue is generally considered a positive sign, indicating that the company is growing and performing well. Conversely, a decrease in revenue is often seen as a warning sign, indicating that the company may be facing financial difficulties.
Revenue is calculated by multiplying the quantity of goods or services sold by the selling price, and then adding up the results for all sales during the period in question. It is important to note that revenue is recorded when it is earned, not when payment is received.In conclusion, revenue is a key financial metric that provides important information on the financial performance of a company. It is used to evaluate the company's ability to generate income and is a key factor in determining its financial stability and growth potential.
2. COST OF GOODS SOLD
The next section lists the direct costs associated with producing and selling the company's products or services. This can include raw materials, labor costs, and manufacturing overhead. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is a term used in accounting to represent the direct costs associated with producing and selling a product. It is a key component in determining the gross profit of a company and is typically reported on a Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, also known as an income statement.COGS includes the cost of raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead that are directly attributed to the production of goods.
This amount is subtracted from the revenue generated from the sale of those goods to determine the gross profit of the company.The calculation of COGS is important because it provides a snapshot of the efficiency and profitability of a company's operations. A high COGS compared to revenue indicates that the company may be producing and selling products at a higher cost than its competitors, while a low COGS suggests that the company is operating more efficiently.In conclusion, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is a critical component of a company's financial performance and is used to evaluate the efficiency and profitability of its operations. Understanding COGS is important for companies and investors alike, as it provides a key metric for determining the overall financial health and stability of a business.
3.GROSS PROFIT
This section calculates the amount of money earned by the company before subtracting operating expenses. Gross profit is calculated by subtracting COGS from revenue. Gross profit is a key financial metric that represents the amount of money a company earns from its sales, after subtracting the cost of the goods sold. It is calculated by subtracting the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) from the revenue generated from the sale of those goods.
Gross profit is important because it provides a snapshot of the profitability of a company's operations, before accounting for other expenses such as marketing, administration, and overhead costs. A high gross profit compared to revenue indicates that the company is operating efficiently and earning a good margin on its products, while a low gross profit suggests that the company is struggling to cover its costsGross profit is typically reported on a Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, also known as an income statement, and is used by investors and analysts to evaluate the financial performance of a company. It is also used by companies to make informed decisions about pricing, product mix, and other aspects of their operations.In conclusion, gross profit is a key metric for evaluating a company's financial performance and provides important information on the efficiency and profitability of its operations. Understanding gross profit is important for companies and investors alike, as it provides a snapshot of the company's bottom line before accounting for other expenses.
4. OPREATING EXPENSE
This section lists the indirect costs associated with running the company's operations, such as marketing, research and development, rent, and utilities. Operating expenses, also known as operating costs, are the costs incurred by a company in the normal course of its business operations. They are expenses that are not directly associated with the production of goods or services and are reported on a Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, also known as an income statement.Operating expenses include costs such as marketing, administration, sales, and research and development. They also include depreciation and amortization of assets, such as buildings, equipment, and intangible assets.
The calculation of operating expenses is important because it provides a snapshot of the efficiency and profitability of a company's operations. A high level of operating expenses compared to revenue indicates that the company is spending more on its operations than its competitors, while a low level of operating expenses suggests that the company is operating more efficiently.In conclusion, operating expenses are a critical component of a company's financial performance and are used to evaluate the efficiency and profitability of its operations. Understanding operating expenses is important for companies and investors alike, as it provides a key metric for determining the overall financial health and stability of a business.
5. OPREATING INCOME
This section calculates the amount of money earned by the company after subtracting operating expenses from gross profit.
6. OTHER INCOME/EXPENSE
This section lists any other income or expenses not associated with the company's core operations, such as interest income, investment gains or losses, and tax expenses. Other income/expense is a line item on a Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, also known as an income statement, that includes all income and expenses that are not related to the company's core operations. These items may include interest income from investments, gains or losses from the sale of assets, and foreign exchange gains or losses.Other income/expense can have a significant impact on a company's overall financial performance, as it includes items that are not part of the company's normal operations. For example, a gain from the sale of an asset could increase a company's net income, while a loss from foreign exchange could decrease it.
It is important to consider other income/expense when evaluating a company's financial performance because it provides a more complete picture of the company's financial health and stability. Investors and analysts use this information to make informed decisions about a company's financial performance and future prospects.In conclusion, other income/expense is a critical component of a company's financial performance and is used to evaluate the efficiency and profitability of its operations. Understanding other income/expense is important for companies and investors alike, as it provides a key metric for determining the overall financial health and stability of a business.
7. NET INCOME
This section calculates the final profit or loss for the period being reported. Net income is calculated by subtracting all expenses from revenue, including COGS, operating expenses, and other income/expense. Net income, also known as net profit, is the final result of a company's financial performance as reported on a Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, also known as an income statement. It represents the amount of money a company earns from its operations, after accounting for all of its revenue and expenses.Net income is calculated by subtracting all expenses, including cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and other income/expense, from the company's total revenue.
The result is the net income, which represents the company's bottom line.Net income is a critical metric for evaluating a company's financial performance and is used by investors and analysts to determine the profitability of a company. A high net income indicates that a company is profitable, while a low net income suggests that the company is struggling to generate profits.In conclusion, net income is a key financial metric that provides a snapshot of a company's financial performance and is used to evaluate the efficiency and profitability of its operations. Understanding net income is important for companies and investors alike, as it provides a final result of the company's financial performance and is a key factor in determining its financial health and stability.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN GROSS PROFIT AND NET PROFIT
Gross Profit and Net Profit are two important metrics that measure the financial performance of a company. The main difference between them is as follows:
Gross Profit: Gross profit is the profit a company earns after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from its revenue. It measures the amount of money a company makes from its core operations before subtracting operating expenses. Gross profit is an important indicator of a company's pricing strategy and production efficiency.
Net Profit: Net profit, also known as net income, is the final profit a company earns after deducting all expenses from its revenue, including COGS, operating expenses, and other income/expense. It measures the amount of money a company makes after accounting for all costs associated with running its operations. Net profit is an important indicator of a company's overall financial health and is used to evaluate its performance and profitability.
In conclusion, gross profit and net profit are two distinct measures of a company's financial performance. Gross profit provides a snapshot of a company's ability to earn money from its core operations, while net profit provides a more comprehensive picture of a company's financial performance, including all costs associated with running its operations. Understanding the difference between gross profit and net profit is important for companies, investors, and other stakeholders as they evaluate a company's financial health and performance.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the Profit and Loss (P&L) statement is a critical financial document that provides a snapshot of a company's financial performance over a specific period of time. It summarizes the company's revenue, expenses, and profits or losses. By reviewing a P&L statement, stakeholders can evaluate a company's financial health, assess its ability to generate revenue, and determine its profitability.The P&L statement is also an important tool for management to make informed decisions about the company's operations and future growth. By analyzing the different components of a P&L statement, such as revenue, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and net income, management can identify areas of improvement, set goals and objectives, and allocate resources effectively. Overall, the P&L statement is a valuable resource for understanding a company's financial performance and making informed decisions about its future. Understanding the components and format of a P&L statement is essential for companies, investors, and other stakeholders as they evaluate a company's financial health and performance.